

OLSSON'S IS CLOSED
Thank you to all our loyal customers who supported us for 36 years
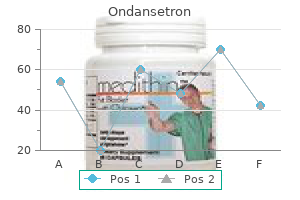
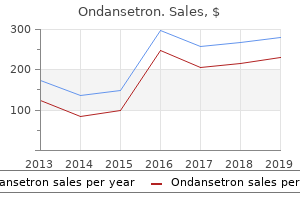
"Buy generic ondansetron 4mg line, medications held before dialysis".
By: V. Folleck, M.A., M.D.
Assistant Professor, Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
The presence or absence of a dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial pulse is the simplest and most dependable indicator of great ischemia that can be elicited on the bedside medicine 75 yellow cheap ondansetron online american express. Approximately 5% to 10% of diabetic sufferers have had past or present foot ulceration 909 treatment buy generic ondansetron pills, and 1% have undergone amputation medications not to take with grapefruit buy ondansetron 4mg with mastercard. A massive community-based examine within the United Kingdom showed an annual incidence of ulceration of roughly 2%; this rose to 7% with recognized diabetic neuropathy and to as excessive as 50% with a previous history of ulceration treatment lichen sclerosis order 8 mg ondansetron free shipping. Even in experienced diabetic foot clinics, greater than 50% of sufferers with new foot ulcers give a previous ulcer historical past. OtherDiabeticComplications Patients with retinopathy and renal dysfunction are at increased risk for foot ulceration. A and B, Two lateral views of a affected person with typical indicators of a high-risk neuropathic foot. Notice the small-muscle wasting, clawing of the toes, and marked prominence of the metatarsal heads. At presentation with type 2 diabetes mellitus, this affected person had severe neuropathy with foot ulceration on both the proper foot (shown here) and the left foot. The mixture of proprioceptive loss as a end result of neuropathy and the prominence of metatarsal heads leads to increased pressures and loads beneath the diabetic foot. High pressures, along with dry skin, typically outcome in the formation of callus under weight-bearing areas of the metatarsal heads. The presence of such plantar callus has been proven in cross-sectional and prospective studies to be a highly vital marker of foot ulcer danger. Conversely, removing of plantar callus is associated with a discount in foot pressures and subsequently a discount in foot ulcer risk. In 1999, a North American/United Kingdom collaborative study1006 assessed the danger factors that resulted in ulceration in more than 150 consecutive foot ulcer cases. From this research, numerous causal pathways had been identified, however the most typical triad of element causes- neuropathy, deformity, and trauma-was current in 63% of incident ulcers. Because foot ulcers precede most amputations, are among the most typical causes of hospital admission for patients with diabetes, and account for much morbidity and even fatality, the widespread software of preventive foot care methods is urgently required. Patients with any kind of diabetes require regular evaluation and screening of the toes for evidence of threat factors for foot ulceration, regardless of disease duration. Of all the long-term problems of diabetes, foot problems and their threat components are probably the easiest to detect. No costly equipment is required, and the feet can be examined for evidence of neuropathic and vascular deficits within the office setting utilizing simple gear. A easy neurologic examination ought to embrace evaluation of pressure perception utilizing a 10-g monofilament; in a large U. A comparability of two diabetic foot ulcer classification methods: the Wagner and the University of Texas wound classification methods. Comprehensive foot examination and threat evaluation: a report of the Task Force of the Foot Care Interest Group of the American Diabetes Association, with endorsement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. The orthotist, or shoe fitter, is invaluable to advise about and sometimes design footwear to shield high-risk ft, and these members of the team ought to work intently with the diabetologist and the vascular and orthopedic surgeons. Patients with threat components for ulceration require preventive foot care training and frequent review. Basically, a diabetic foot ulcer will heal if the following three conditions are happy: � Arterial inflow is sufficient. Although this strategy might seem simplistic, failure of diabetic foot ulcers to heal is often a results of failure to pay adequate attention to a number of contributing circumstances, including strain on the wound, infection, ischemia, and inadequate d�bridement. The most common cause of nonhealing of neuropathic foot ulcers is the failure to take away stress from the wound and quick surrounding area. Pain results in safety of an injured space; the dearth of ache permits strain to be put immediately onto the ulcer and leads to nonhealing. A patient with normal sensation and a foot wound will limp to avoid placing stress on the wound as a result of doing so is painful; hence, the observation is made initially in leprosy, and more recently in diabetic neuropathy, that a patient who walks on a plantar wound with out limping should have neuropathy. No risk factor Yes risk issue Provide general recommendation � Nail care, hygiene � Footwear � Podiatry � Foot care training � Regular podiatry � Possible special footwear, hosiery, etc. The impact of stress reduction on the histopathologic features of neuropathic ulcers was assessed in a randomized examine.
History Quality of chest ache typically worse on inspiration and in sure postures medicine shoppe buy ondansetron 8mg on line, for instance lying back Was there a viral prodrome (fever medications jamaica purchase 8 mg ondansetron visa, malaise medications you can take during pregnancy buy ondansetron 8mg otc, sore throat medications that cause weight loss cost of ondansetron, muscle aching) This is uncommon, and is usually because of spread of intrathoracic infection, for example following thoracic trauma or complicating bacterial pneumonia. Consider tuberculous or fungal an infection if the effusion is purulent however no organisms are seen on Gram stain. Acute pericarditis 343 3 Possible Dressler (postpericardiotomy) syndrome Consider Dressler syndrome if the affected person has had recent cardiac surgery (typically 2�4 weeks previously). It could additionally be preceded by a flu-like sickness and is normally a self-limiting disorder lasting 1�3 weeks. Colchicine must be co administered, and continued for three months, to cut back the chance of recurrence (Table 53. Have a high index of suspicion in the presence of predisposing circumstances (Table fifty four. It may be palpable within the radial artery, with the radial pulse disappearing on inspiration. Patients with malignant effusions will often require further intervention to prevent recurrent tamponade, for example chemotherapy or creation of a pericardial window. Problems Signs of tamponade but solely small pericardial effusion (echo separation <10 mm) this will happen with effusive-constrictive pericarditis in malignancy, autoimmune illness and after viral infection. Bleeding into the pericardial area Penetrating and blunt chest trauma, including external cardiac compression Bleeding from a cardiac chamber or coronary artery brought on by perforation or laceration as a complication of cardiac catheterization, percutaneous coronary intervention, pacemaker insertion, pericardiocentesis or central venous cannulation Bleeding after cardiac surgical procedure Cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction Aortic dissection with retrograde extension into pericardial house Anticoagulant remedy for atrial fibrillation or different indication in the presence of pericarditis Thrombolytic therapy given (inappropriately) for pericarditis Serous or sero-sanguinous pericardial effusion Neoplastic involvement of the pericardium (most generally in carcinoma of breast or bronchus, or lymphoma or cardiac angiosarcoma) Pericarditis complicating connective tissue ailments. Presence, dimension and distribution (circumferential or loculated) of pericardial fluid Be conscious that a pleural effusion or dilated right ventricle may be misdiagnosed on echocardiography as a pericardial effusion Are there echocardiographic signs of cardiac tamponade in a spontaneously respiratory subject Drainage may be troublesome if the fluid is dense or there are a number of loculations. Echocardiography can be utilized to guide pericardiocentesis by confirming the position of the needle tip from the presence of intra-pericardial bubbles on re-injection of the initial fluid sampled, and must be repeated after drainage to assess the size of any residual effusion. Tamponade with severely impaired left ventricular perform Total pericardiocentesis could result in further ventricular dilatation. Acute administration is determined by the scientific context and the presence and type of organ harm. Intravenous therapy has specific indications, but is doubtlessly dangerous, as an abrupt reduction in blood strain may trigger cerebral, myocardial and renal ischaemia. Priorities Establish the context and comorbidities by centered medical assessment and investigation (Tables fifty five. Acute aortic dissection � Make sure enough analgesia has been given, as ache will contribute to hypertension. Acute ischaemic stroke � See Chapter 65 for the evaluation of the affected person with ischaemic stroke. What investigations have been accomplished to exclude an underlying trigger for hypertension Examination � Measure the blood pressure in each arms � Check for signs of coronary heart failure and aortic regurgitation � Check the presence and symmetry of the major pulses, and for radio-femoral delay � Listen for carotid, abdominal and femoral bruits � Examine the abdomen (palpable kidneys Blood glucose Sodium, potassium and creatinine (check daily), low Na and K in hyperaldosteronism and renal artery stenosis Plasma troponin, if acute coronary syndrome suspected Full blood depend Plasma renin/aldosterone (for later analysis) Urine stick test and microscopy (renal impairment with minimal proteinuria suggests renal artery stenosis) Ultrasonography of kidneys and urinary tract Urinary catecholamine excretion Urinary free cortisol excretion if suspected Cushing syndrome (Table 55. Hypertensive encephalopathy is due to cerebral oedema resulting from hyperperfusion, as a consequence of severe hypertension, with failure of autoregulation of cerebral blood move. Hypertensive encephalopathy is favoured by the gradual onset of signs and the absence (or late appearance) of focal neurological signs. In hypertensive encephalopathy, neurological status improves with reducing of blood strain. Early options � Headache � Nausea and vomiting � Delirium � Retinal haemorrhages, exudates or papilloedema Late features � Focal neurological indicators � Fits � Coma Severe hypertension 351 Suspected pre-eclampsia/eclampsia: being pregnant or inside three months of giving start � the diagnosis of pre-eclampsia/eclampsia is discussed in Chapter 32. Cocaine-induced hypertension � Sedation with a benzodiazepine is the popular initial treatment for cocaine-induced hypertension. Other patients 1 Admit for investigation and administration if there are any of the following features: � Retinal haemorrhages, exudates or papilloedema � Acute kidney injury � Interstitial pulmonary oedema � Diastolic pressure >130 mmHg Recheck the blood stress after the affected person has rested for 30 min in a quiet room. Causes of secondary hypertension, and clues to specific diagnoses, are summarized in Table 55. Clinical setting Phaeochromocytoma suspected (see Chapter 94) Renal artery stenosis suspected (see Table fifty five. Cause Intrinsic renal disease Clues/investigation Family historical past of heritable renal disease. Further administration Anticoagulation Anticoagulation is mentioned intimately in Chapter 103. Anticoagulation for deep vein thrombosis could be with rivaroxaban, low-molecular-weight heparin or warfarin (preceded by and overlapping with heparin). Clinical feature History Active most cancers (treatment ongoing, or within previous 6 months, or palliative) Paralysis, paresis or recent plaster immobilization of the leg Recently bedridden for more than 3 days, or major surgery within four weeks Examination Localized tenderness alongside the distribution of the deep venous system Entire leg swollen Calf swelling by >3 cm compared with asymptomatic leg (measured 10 cm below tibial tuberosity) Pitting oedema (greater within the symptomatic leg) Collateral superficial veins (non-varicose) Alternative diagnosis Value of assessment of pretest chance of deep-vein thrombosis in medical administration.
Transcriptional regulation of the adipocyte fatty acid synthase gene by agouti: interplay with insulin symptoms 8 days past ovulation cheap ondansetron 8mg without a prescription. Progressive histopathological changes in pancreatic islets of Zucker diabetic fatty rats acne natural treatment buy discount ondansetron on line. Basal insulin hypersecretion in insulin-resistant Zucker diabetic and Zucker fatty rats: function of enhanced fuel metabolism medications high blood pressure buy ondansetron on line. Effect of dietary fat on the event of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in overweight Zucker diabetic fatty male and female rats treatment skin cancer discount ondansetron 4 mg line. Underexpression of beta cell excessive Km glucose transporters in noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Evidence that down-regulation of beta-cell glucose transporters in non-insulin-dependent diabetes could additionally be the cause for diabetic hyperglycemia. Effects of troglitazone on substrate storage and utilization in insulin-resistant rats. Lipoapoptosis in beta-cells of overweight prediabetic fa/fa rats: role of serine palmitoyltransferase overexpression. Prevention of hyperglycemia in the Zucker diabetic fatty rat by treatment with metformin or troglitazone. Effects of age, pressure, and dietary carbohydrate on the hepatic metabolism of male rats. Defects in liver and muscle glycogen metabolism in neonatal and adult New Zealand obese mice. The biochemical basis of elevated hepatic glucose manufacturing in a mouse model of type 2 (non-insulindependent) diabetes mellitus. Impaired regulation of hepatic fructose-1,6-biphosphatase in the New Zealand overweight mouse: an acquired defect. Glucose and lipid metabolism within the gold-thioglucose injected mouse mannequin of diabesity. Constitutive and impaired signaling of leptin receptors containing the Gln Pro extracellular area fatty mutation. Cataract growth in diabetic sand rats treated with alpha-lipoic acid and its gammalinolenic acid conjugate. Cellular mechanism of nutritionally induced insulin resistance in Psammomys obesus: overexpression of protein kinase Cepsilon in skeletal muscle precedes the onset of hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia. Hyperinsulinemia induces a reversible impairment in insulin receptor operate resulting in diabetes in the sand rat mannequin of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A major quantitative trait locus co-localizing with cholecystokinin sort A receptor gene influences poor pancreatic proliferation in a spontaneously diabetogenic rat. Sexual difference within the incidence of diabetes mellitus in Otsuka-Long-Evans-Tokushima-Fatty rats: results of castration and intercourse hormone substitute on its incidence. Effects of weight problems and inheritance on the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Otsuka-Long-Evans-Tokushima fatty rats. Troglitazone and metformin, but not glibenclamide, lower blood stress in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Experimental chemical diabetes and being pregnant within the rat: evolution of glucose tolerance and insulin response. Chemical diabetes in the grownup rat as the spontaneous evolution of neonatal diabetes. Spontaneous restoration from noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced by neonatal streptozotocin remedy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the development of diabetic microvascular issues in Japanese sufferers with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6-year study. Intensive glucose management and issues in American veterans with sort 2 diabetes. Effect of intensive management of glucose on cardiovascular outcomes and demise in patients with diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomised managed trials. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology-clinical follow tips for creating a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan, 2015. Defining the relationship between plasma glucose and HbA1c: analysis of glucose profiles and HbA1c within the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Effects of size, time of day and sequence of meal ingestion on carbohydrate tolerance in normal subjects. Costs and advantages associated with diabetes schooling: a evaluation of the literature.
Buy ondansetron 8 mg mastercard. Health Anxiety: Why Your Symptoms Wont Go Away.
Syndromes
Otherwise treatment 7th feb cardiff discount ondansetron amex, the displacement could additionally be seen as a radiolucency (slightly decrease density than gentle tissue or effusion) within the shape of the part 7 medications that can cause incontinence discount 4mg ondansetron overnight delivery, displacing different buildings alternative medicine cheap 8 mg ondansetron amex, or wedged between part of the joint medications quit smoking generic 4mg ondansetron with visa, resulting in locking or widening. Initial Placement of Components Initial placement of the arthroplasty parts is crucial to their long-term success. Generally speaking, the elements are placed such that they mimic the location of the original nonpathologic joint, permitting stabilizing constructions and muscles to exert their regular stresses across the components. However, some constructs, even when appropriately positioned, may not seem to be "anatomically" located. It is essential to correctly understand and consider the expected postoperative location and angulation of components in addition to associated osteoplasties, which may be required to lower the probability of impingement. Stress shielding has not been shown to correlate with arthroplasty failure or with pain and is considered normal. Implant Fracture Fracture of a component could happen because of instability or abnormal stress. Fractures of a cemented polyethylene component are usually visualized by a fracture in the cement or distortion of the component form (a spherical acetabular cup might turn into extra oval). If the implant is polyethylene with skinny metal backing (patellar buttons are one example), the steel backing might fragment or fracture and will carry the polyethylene attachment with it when it separates. The threat increases with prolonged operative time as nicely as with a quantity of incisions and operative sites. The signs usually bring the patient to medical attention prior to developing radiographic changes. If there are radiographic abnormalities, they embrace effusion, serpiginous osseous destruction, periosteal reaction, and endosteal bone response. Fluffy, immature, periarticular heterotopic bone formation could be suggestive of the prognosis. All cement from the arthroplasty must be removed as properly because it may remain as a nidus for continual an infection. The cement could additionally be shaped in beads connected by a string or may be formed as a spacer to keep normal spacing between residual bone surfaces. An contaminated hip may be left with the residual femoral shaft in a muscle sling, termed a Girdlestone. Once the full treatment for infection is completed, the affected person could also be reimaged or reaspirated to rule out residual an infection previous to placement of a revision arthroplasty. Polyethylene put on is identified by remark of differential thinning in the weight-bearing area compared with different regions of the part. Specifically, acetabular polyethylene put on usually occurs differentially on the superolateral and anterior parts of the part compared to the inferomedial portion. Silastic implants utilized in small joints of the hand and foot are sometimes not anchored to bone. Abnormal movement as well as the thinness of parts of these components frequently leads to breakdown of the implants. A element could "subside" into the underlying bone, shifting superiorly (acetabular cup, patellar button), inferiorly (femoral or tibial components), or in a medial-lateral path. Subtle tilt or subsidence could additionally be noted only when the image is in contrast with an older index image obtained soon after the position of the parts. Loosening of a component can also be seen as a lucency on the interface between bone and cement or the interface between bone and element. Fractured cement additionally indicates significant factor movement and related loosening. This is taken into account regular unless the bone hypertrophy is so intensive that it bridges the medullary canal; in that case, loosening should be suggested. Overall, it is suggested that if bone-component lucency and hypertrophic change are judged to not represent true loosening, the findings should be followed to see if stability is Particle Disease Particle illness outcomes from particles of a critical dimension triggering an inflammatory reaction and synovitis, which in turn might set off soft tissue necrosis &/or large osteolysis. The origin of the particles appears immaterial; osseous debris, cement fragments, steel particles (including beads), and polyethylene or Silastic particles might all be of the appropriate size to initiate the response. The particles incite an inflammatory response in periprosthetic tissues, resulting in secretion of cytokines, development components, and enzymes; these promote formation of osteolytic granulomas. The repetitive hydraulic impact of joint fluid brings reactive tissue in contact with prone bone.